What are Learning Outcomes?
Learning outcomes are specific statements of what students will be able to do when they successfully complete a learning experience (whether it's a project, course or program). They are always written in a student-centered, measurable fashion that is concise, meaningful, and achievable.
Learning Outcomes at the University or Program Level
Outcomes are used on many scales, from developing curriculum for a program of study to creating lessons for a single class activity. At the highest level, learning outcomes can be established at the university level. You can review the learning outcomes for DePaul graduates at the institutional level or program level.
Learning Outcomes at the Module, Unit, or Week Level
Just as learning outcomes can be designed at the program level or university-wide level, they can also operate at a more granular scale within an individual course. Typically instructors divide their courses into smaller units such as modules or weeks, and many instructors establish learning outcomes for these smaller units that map onto the larger course-level outcomes. As a general rule, as the level of analysis becomes smaller, from course to module to assignment, the learning outcomes tend to be more specific and easily quantifiable.
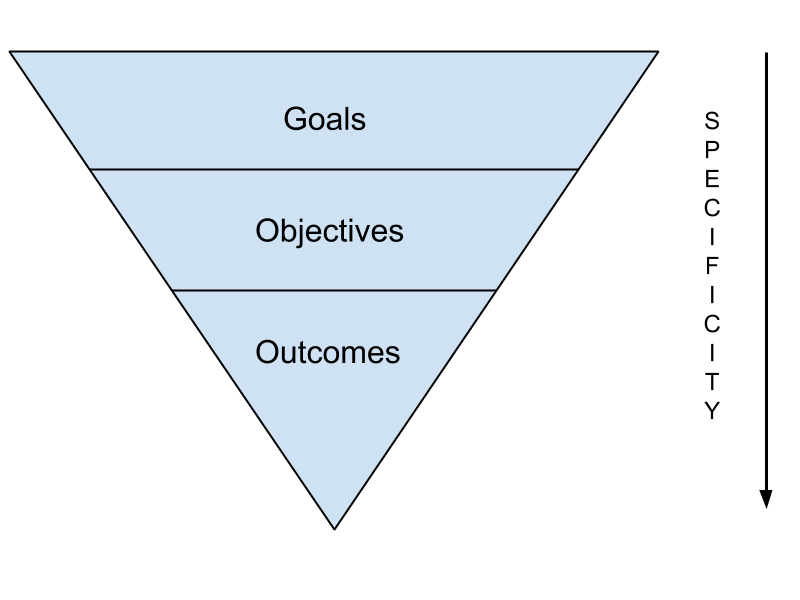
How are Learning Outcomes Different from Learning Goals or Learning Objectives?
These terms are often used interchangeably and they are all related to the teaching and learning that is expected to take place in the classroom. However, the difference between goals or objectives and outcomes lies in the emphasis on who will be performing the activities.Learning goals and objectives generally describe what an instructor, program, or institution aims to do, whereas, a learning outcome describes in observable and measurable terms what a student is able to do as a result of completing a learning experience (e.g., course, project, or unit).
Learning goals are broad statements written from an instructor's or institution's perspective that give the general content and direction of a learning experience. They generally describe what an instructor or program aims to do; i.e., “The curriculum will introduce students to the major research methods of the discipline.”
Learning objectives are statements of what you intend to teach or cover in a learning experience. They tend to be
- More specific than learning goals
- Not necessarily observable nor measurable
- Instructor-centered rather than student-centered
- Useful in helping you formulate more specific learning outcomes
Examples
- We will cover historical perspectives and debates about the role of mass communication in the 20th century.
- Students will understand the impacts and effects of new media on identity formation.
Learning objectives can introduce unintended complexity because sometimes they are written in terms of what you intend to teach (the first example above) and sometimes they are written in terms of what you expect students will learn (the latter example). In contrast, learning outcomes should always be written with a focus on the learner and how the learner will demonstrate achievement, which makes it easier to assess students' learning.
Why Write Learning Outcomes?
Identifying the desired results of a learning experience is the first step of backward design.Learning outcomes are used for this purpose. Learning outcomes are also valuable in these ways:
Learning outcomes help instructors...
- describe to students what is expected of them
- plan appropriate teaching strategies, materials and assessments
- learn from and make changes to curriculum to improve student learning
- assess how the outcomes of a single course align with larger outcomes for an entire program
Learning outcomes help students…
- anticipate what they will gain from an educational experience
- track their progress and know where they stand
- know in advance how they'll be assessed
Elements of Effective Learning Outcomes
Clearly written course-level and module-level outcomes are the foundation upon which effective courses are designed. Outcomes inform both the way students are evaluated in a course and the way a course will be organized. Effective learning outcomes are student-centered, measurable, concise, meaningful, achievable and outcome-based (rather than task-based).
Outcomes are phrased from the perspective of the student and are written in language that can be easily understood by them.
Outcomes are specific, observable, and can be assessed. They use a concrete action verb.
Outcomes are written in short, succinct sentences.
Outcomes emphasize higher-order thinking and are consistent with university, college, department, and program learning outcomes.
The total number of outcomes is reasonable for this population of students and is achievable within the time available.
Outcomes should specify the skills and knowledge students must demonstrate to prove mastery instead of focusing on the assignment format, such as a quiz or essay. Well-worded outcomes should remain flexible enough to accommodate a variety of formats for a corresponding assessment.
Writing Learning Outcomes
While designing a course, instructors are most likely to develop course-level outcomes, which is to say the level of analysis is the course as opposed to the program of study (at a higher level) or module/week (at a lower level)
Formula for Writing Learning Outcomes
|
| As a result of participating in (educational unit), students will be able to (measurable verb) + (learning statement). |
If the educational unit is implied, based on the context in which the learning outcomes are shared, you might leave off the first portion of the learning outcome statement.
Example course learning outcomes using this formula:
- As a result of participating in Quantitative Reasoning and Technological Literacy I, students will be able to evaluate statistical claims in the popular press.
- As a result of completing Ethics and Research I, student will be able to describe the potential impact of specific ethical conflicts on research findings.
- As a result of completing Money and Banking, students will be able determine the cost benefits and shortcomings of various cash management strategies.
Example module- or unit-level learning outcome using this formula:
- By the end of unit 4, students will be able to explain the relationship between significance levels and the null hypothesis.
- By the end of module 3, students will be able to render a video clip with a compression level appropriate for web-based viewing.
- By the end of week 2, students will be able to calculate standard deviation from the mean.
- By the end of unit 8, students will be able to recommend an appropriate treatment based on patients' symptoms.
- By the end of week 6, students will be able to build a case for or against charter schools based on interpretation of recent research
Examples of Common Learning Outcome Problems and Solutions
Not Student-CenteredDifferent theories of personality development will be explored through lectures, readings, and assignments. |
Student-CenteredStudents will name each theory of personality development and describe the key characteristics that distinguish each theory. |
Not MeasurableStudents will understand symbolism. |
MeasurableStudents will be able to identify examples of symbolism in short stories and incorporate symbolism in their own writing. |
Not Clear
Students will be able to analyze American history.
|
ClearStudents will be able to analyze how American foreign policy history relates to current trends in American foreign policy. |
Not ConciseStudents will analyze American foreign policy, from 18th-century diplomatic relations with Europe to the Monroe Doctrine, considering the ways in which shifts from expansionism and Manifest Destiny to isolationism and protectionism impacted relations with neighboring nations and Native Americans. |
ConciseStudents will be able to identify how changes in American foreign policy during the 18th and 19th centuries impacted relations with neighboring nations and Native Americans. |
Task-Based (Inflexible)Students will be able to demonstrate on a mannequin the four steps to administer CPR. |
Outcome-Based (Flexible)Students will be able to demonstrate the four steps used to administer CPR. |
The Center for Teaching and Learning is available to consult with departments and individual faculty members on developing learning outcomes.
Concrete Action Verbs
The following list includes concrete action verbs that correspond with each level of Bloom's taxonomy for the cognitive domain. To ensure outcomes are measurable, you might find it helpful to start each one with a verb from this list.
compose, construct, create, design, develop, integrate, invent, make, manage, modify, prepare, propose, synthesize
assess, choose, convince, critique, decide, determine, defend, estimate, judge, justify, measure, predict, prioritize, prove, rate, recommend, select
analyze, categorize, compare, contrast, deconstruct, differentiate, examine, infer, organize, select, test
apply, carry out, choose, demonstrate, recreate, show, solve, use
describe, distinguish, clarify, classify, compare, convert, contrast, estimate, explain, identify, locate, predict, relate, report, restate, translate, summarize
define, describe, identify, label, list, match, name, order, recall, recognize
What about Hard-to-Measure Outcomes?
Some faculty find it stifling to only include measurable outcomes in their course-planning process. You might have learning goals in mind that are valuable but more difficult to measure in a quarter, such as
- appreciate the intangible benefits of art in society.
- question one's own beliefs and recognize personal bias.
- understand the value of ethics in business leadership.
These are all excellent examples of worthwhile goals that you might integrate into many of your learning materials and activities. It's fine to include hard-to-measure goals like these alongside your course outcomes, but it's best to keep them under a separate heading—such as "Learning Goals"—than to include them with your measurable outcomes. This separation will clarify that these goals are an important part of your course, but won't necessarily be tied to student grading and evaluation in the same way that the student learning outcomes will be.
Further Reading
- Iowa State University's Center for Excellence in Learning and teaching has
a model of learning objectives, an excellent visualization incorporating action verbs from
Bloom's Taxonomy.
- For more information on what makes for clear, measurable learning objectives, you can also use Arizona State University's Objectives Builder tool.
References
Bloom, B. S., Engelhart, M. D., Furst, E. J., Hill, E. J., & Krathwohl, D. R. (Eds.). (1956). Taxonomy of educational objectives: The classification of educational goals. New York, NY: Longmans, Green and Co.